

It may not seem like it, but taking good care of your eyes can be a tricky task. Some factors that contribute to good eye health are within our control, while others are not. Some factors may seem small but have quite large effects. Here are five of the biggest factors that affect your eyes and their health.
If you think you or someone in your family may be experiencing eye issues, schedule an appointment with a Prevea optometrist today. They will be able to accurately diagnose any problems and work with you to create a treatment plan to ensure your eye health is in the best shape possible.
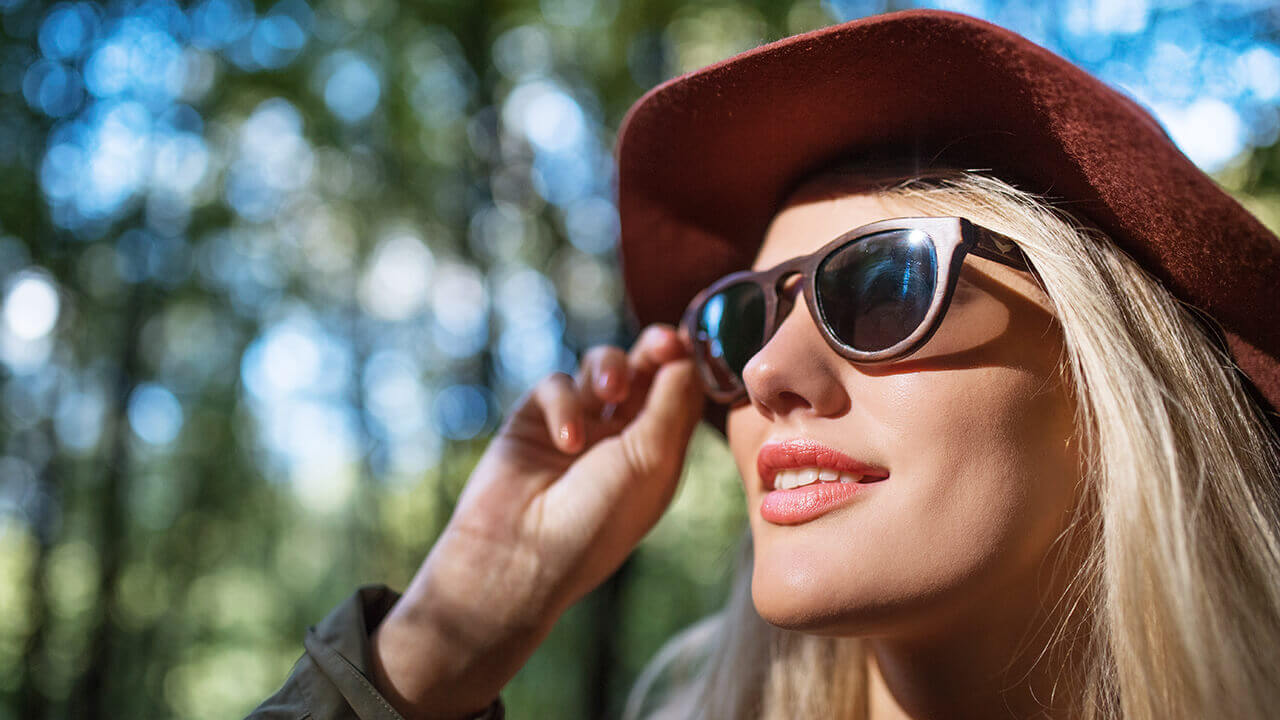
1. UV rays
While the human eye cannot see UV rays, they are known to penetrate the skin and eye tissues, which leads to problems with prolonged exposure. Eye issues that can result from prolonged UV exposure include protein and fat deposits on the eye’s outer layer, cataracts and eyelid cancer. To protect your eyes from UV rays, take these protective measures to block the rays when you’re outside:- Wear a brimmed hat. A simple bucket hat will do the job.
- Wear sunglasses. Consider choosing polarized sunglasses, which are specifically designed to block UV rays and reflections from sun glare.
2. Smoking
Most people know smoking affects the heart and lungs. Did you know it is also damaging to the eyes? Smokers are more than twice as likely to suffer from dry eye syndrome, and those who smoke 15 or more cigarettes per day have an increased risk of cataracts compared to non-smokers. Smokers of all levels are much more likely to develop age-related macular degeneration. Smoking is also a contributing factor to several diseases such as diabetic retinopathy and high blood pressure, which can lead to glaucoma or other issues of the eye. Some of these risks extend to non-smokers living with smokers, too. The damage smoking can do to the eyes can only be stopped by quitting.3. Diet
What you eat can be both a positive and negative factor in eye health. High levels of saturated fat and trans-fat, such as fats found in fried food, can cause buildup and blockages in the blood vessels that supply blood to the eyes. High levels of sodium can contribute to age-related macular degeneration. On the flip side, omega-3 fatty acids found in cold-water fish and tuna help with retinal function and tear production. Zinc, found in red meat, shellfish and nuts, helps in producing melanin – which protects your eyes from light damage. Vitamins C and E are also good for eye health.4. Diabetes
Diabetes damages blood vessels throughout the body, including the eyes. Diabetic retinopathy occurs when blood vessels in the retina become damaged. Those damaged vessels can cause blurry vision because they leak or sometimes stop blood from flowing to the retina. Additionally, macular edema is a common side effect of diabetic retinopathy that can contribute to blurry vision. Other eye issues associated with diabetes include cataracts and glaucoma. To limit your risk of diabetes, do not smoke and keep your blood sugar, blood pressure and cholesterol levels in check. If you are diagnosed with diabetes, early treatment can help mitigate some of its effects on the eyes.5. Genetics
Sometimes, poor eye health is not the result of anything you’ve done – it's just genetic. Common genetic eye issues include color blindness, myopia, hyperopia, glaucoma, cataracts and astigmatism. Most common vision problems that begin early in life are likely linked to genetics, even if that is not the only cause. Genetically related eye problems can also skip generations, meaning that just because your parents experienced great (or poor) vision, it doesn’t mean you will have the same experience. Eye conditions resulting from genetics can most often be treated and managed with medical help – especially if they are caught early.If you think you or someone in your family may be experiencing eye issues, schedule an appointment with a Prevea optometrist today. They will be able to accurately diagnose any problems and work with you to create a treatment plan to ensure your eye health is in the best shape possible.


.jpg?width=500&height=500&ext=.jpg)